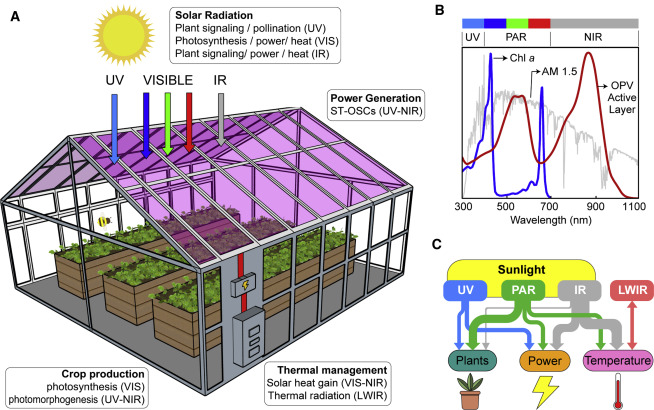
Balancing crop production and energy harvesting in organic solar-powered greenhouses
A recent study shows that lettuce can be grown in greenhouses that filter out wavelengths of light used to generate solar power, demonstrating the feasibility of using see-through solar panels in greenhouses to generate electricity.
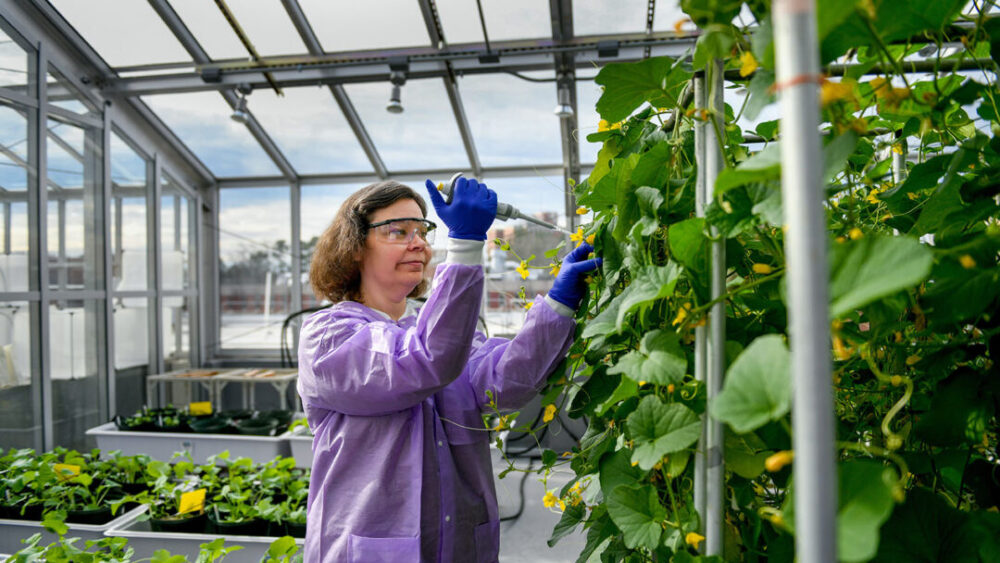
Securely Studying Salmonella to Advance Produce Safety
Kellie Burris is using NC State’s secure greenhouse to study how fresh fruits and vegetables become contaminated with foodborne pathogens before harvesting.
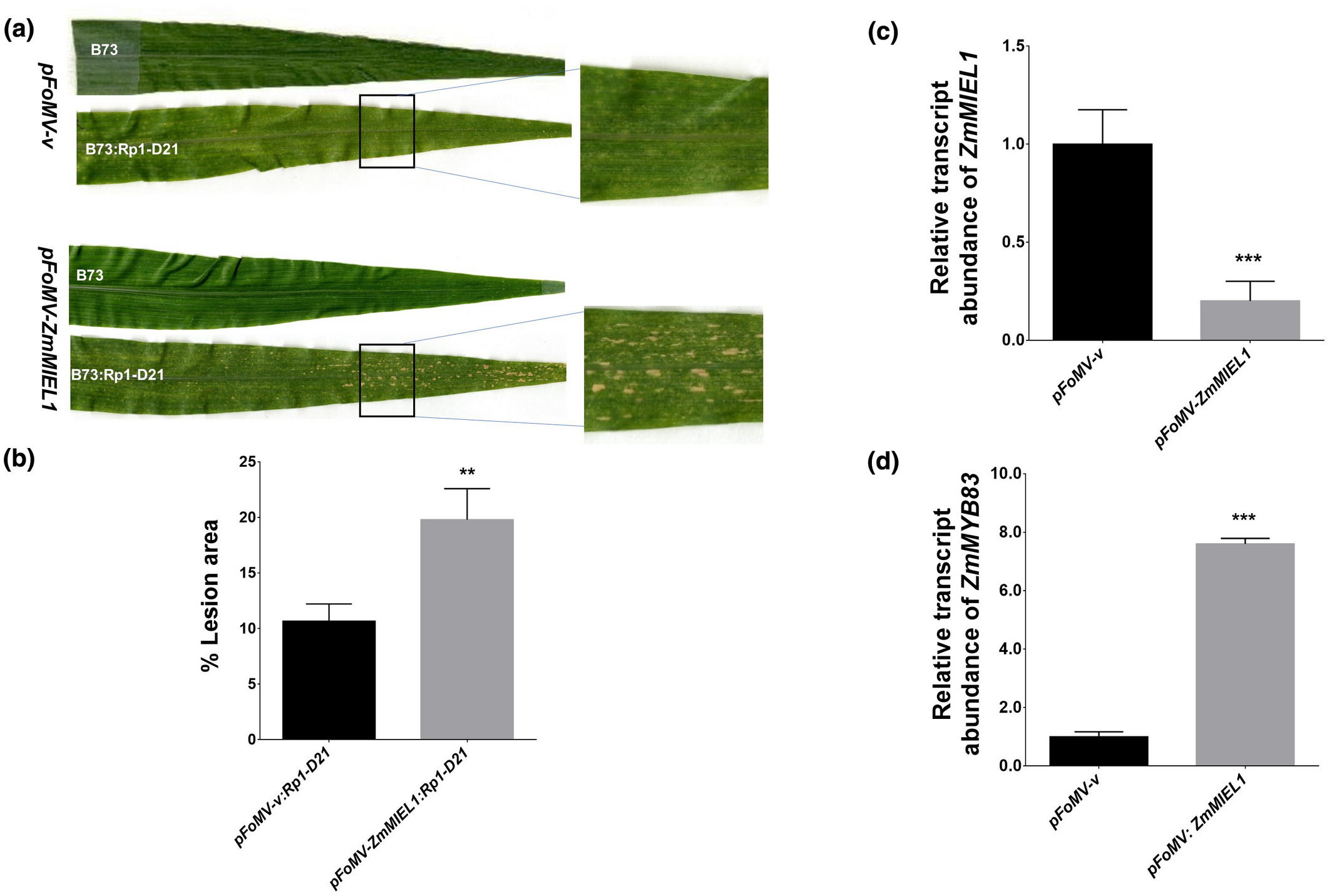
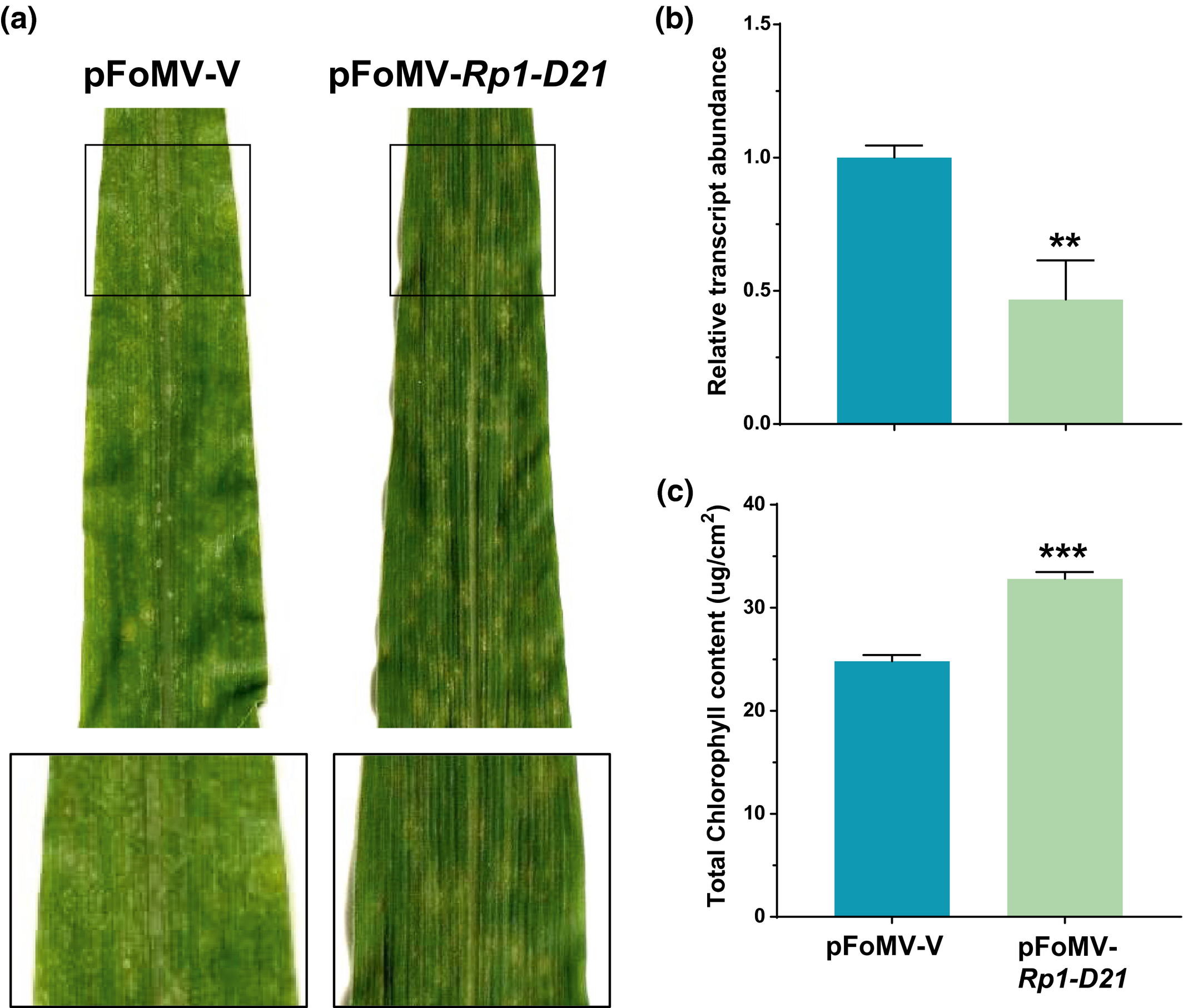
The maize ZmMIEL1 E3 ligase and ZmMYB83 transcription factor proteins interact and regulate the hypersensitive defence response
The present study identifies ZmMIEL1 RING E3 as underlying the effect at one of these loci. It also shows that ZmMIEL1 interacts with and regulates the transcription factor ZmMYB83, which itself can modulate Rp1-D21-induced HR. They characterize the role of both proteins in modulating HR mediated by Rp1-D21 in maize.
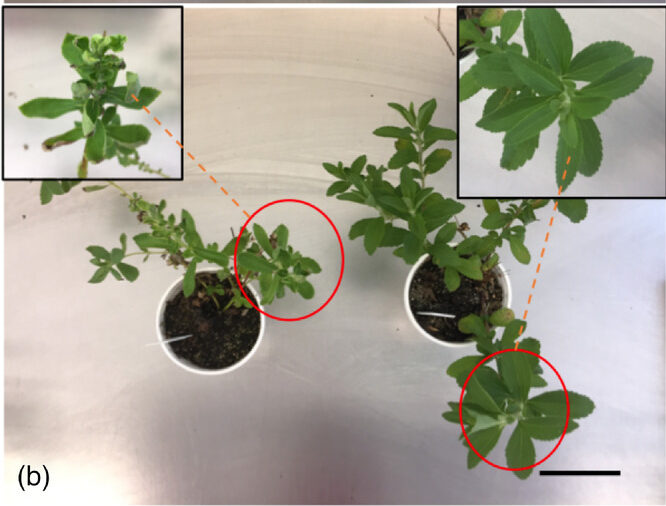
Cold tolerance of diverse stevia cultigens under controlled environment conditions
The objectives of this study were (a) to screen a diverse set of stevia cultigens for cold tolerance at the seedling stage in controlled growth chambers, and (b) to identify optimum combinations of chilling temperature and duration for use in screening and selection.
Use of virus-induced gene silencing to characterize genes involved in modulating hypersensitive cell death in maize
In this study, they report the use of a recently developed system for virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) in maize, based on foxtail mosaic virus (FoMV) (Mei et al., 2016; Mei and Whitham, 2018), to characterize genes associated with Rp1-D21 activity. In this study, we report the use of a recently developed system for virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) in maize, based on foxtail mosaic virus (FoMV) (Mei et al., 2016; Mei and Whitham, 2018), to characterize genes associated with Rp1-D21 activity.
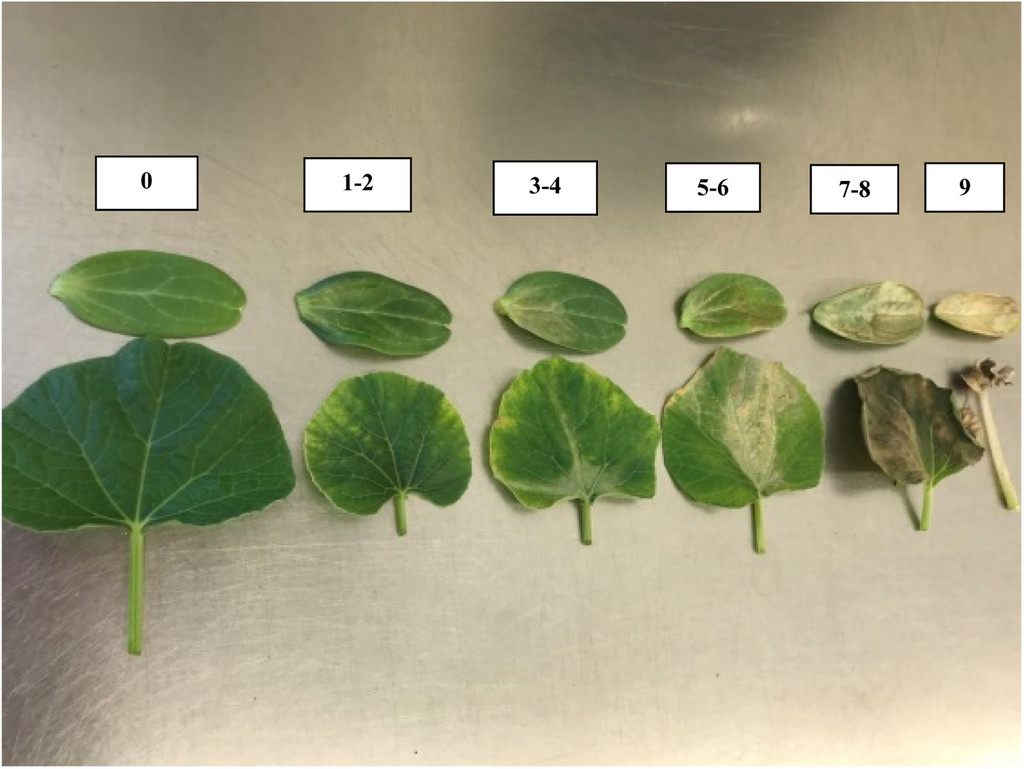
Effects of Cold Durations on Chilling Injury in Lagenaria Germplasm
Tested 163 bottle gourd accessions of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) genebank for cold tolerance in the early seedling stage. The experiment was conducted using controlled environment chambers with 3 chilling durations (36, 48, and 60 hours) at 4 °C. Chilling damage was rated 0 to 9 (0 = no damage, 1 to 2 = trace of damage, 3 to 4 = slight damage, 5 to 6 = moderate damage, 7 to 8 = advanced damage, 9 = plant totally dead).
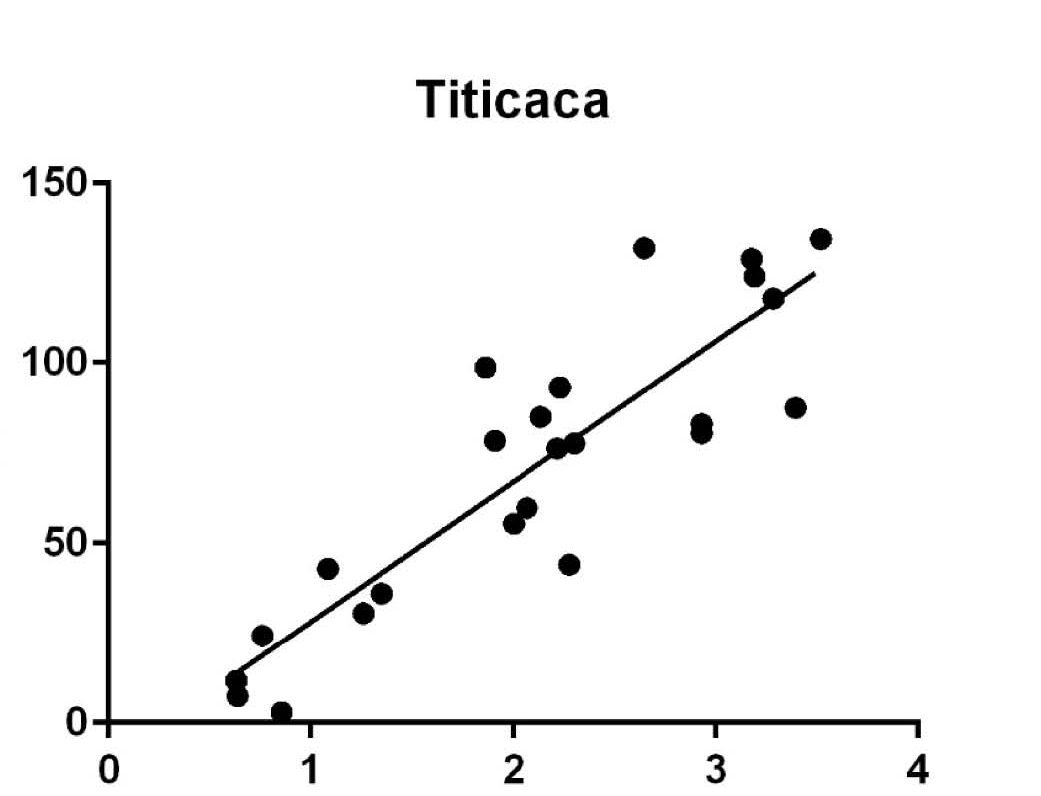
Transpiration response to vapor pressure deficit and soil drying among quinoa genotypes (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.)
The objectives of this study were to differentiate possible differences among eight quinoa genotypes in expression of the two water-conservation traits: (i) partial stomatal closure under elevated VPD levels and (ii) partial stomatal closure at high soil water content.
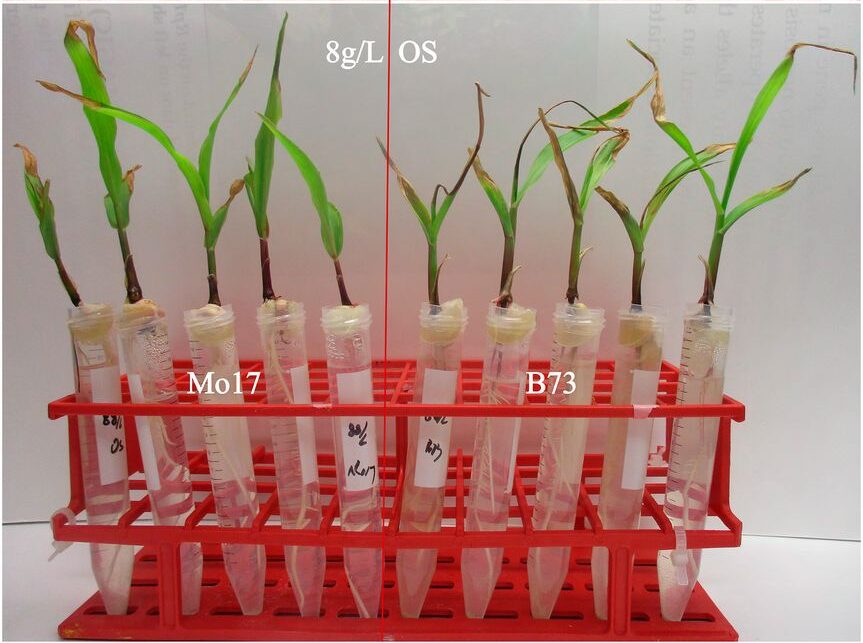
Genetic and Physiological Characterization of a Calcium Deficiency Phenotype in Maize
The goals of this study were: (1) To confirm that the basis of the bull-whip symptoms observed in B73 were due to Ca-deficiency; (2) to characterize the genetic basis of variation in Ca-deficiency between B73 and Mo17.